Revision as of 10:03, 6 May 2023 by Admin (Created page with "Let <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math> be continuous random variables with joint density function <math display = "block"> f(x,y) = \begin{cases} \frac{8}{3}xy, \,\, 0 \leq x...")
May 06'23
Exercise
Let [math]X[/math] and [math]Y[/math] be continuous random variables with joint density function
[[math]]
f(x,y) = \begin{cases}
\frac{8}{3}xy, \,\, 0 \leq x \leq 1, x \leq y \leq 2x \\
0, \, \textrm{Otherwise.}
\end{cases}
[[/math]]
Calculate the covariance of [math]X[/math] and [math]Y[/math].
- 0.04
- 0.25
- 0.67
- 0.80
- 1.24
May 06'23
Solution: A
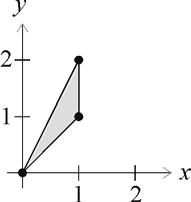
The calculation requires integrating over the indicated region.
[[math]]
\operatorname{E}(X) = \int_0^1\int_x^{2x} \frac{8}{3} x^2 y dy dx = \int_0^{1} \frac{4}{3} x^2y^2 \Big |_x^{2x} dx = \int_0^1 \frac{4}{3}x(4x^2-x^2) dx = \int_0^1 4x^4 dx = \frac{4}{5}x^5 \Big | _0^1 = \frac{4}{5}.
[[/math]]
[[math]]
\operatorname{E}(Y) = \int_0^1\int_x^{2x} \frac{8}{3} x y^2 dy dx = \int_0^{1} \frac{8}{9} xy^3 \Big |_x^{2x} dy dx = \int_0^1 \frac{8}{9}x(8x^3-x^3) dx = \int_0^1 \frac{56}{9}x^4 dx = \frac{56}{45}x^5 \Big | _0^1 = \frac{56}{45}.
[[/math]]
[[math]]
\operatorname{E}(XY) = \int_0^1\int_x^{2x} \frac{8}{3} x^2 y^2 dy dx = \int_0^{1} \frac{8}{9} x^2y^3 \Big |_x^{2x} dx = \int_0^1 \frac{8}{9}x^2(8x^3-x^3) dx = \int_0^1 \frac{56}{9}x^5 dx = \frac{56}{54} = \frac{28}{27}.
[[/math]]
[[math]]
\operatorname{Cov}(X,Y) = \operatorname{E}(XY) - \operatorname{E}(X)\operatorname{E}(Y) = \frac{28}{27} - \left( \frac{56}{45} \right) \left ( \frac{4}{5} \right ) = 0.04.
[[/math]]