Section Logistic Regression discussed logistic regression as a ML method that learns a linear hypothesis map by minimizing the logistic loss. The logistic loss has computationally pleasant properties as it is smooth and convex. However, in some applications we might be ultimately interested in the accuracy or (equivalently) the average 0/1 loss.
Can we upper bound the average [math]0/1[/math] loss using the average logistic loss incurred by a given hypothesis on a given training set?
[math] \newcommand\feature{x} [/math]
Consider a predictor map [math]h(\feature)[/math] which is piece-wise linear and consisting of [math]1000[/math] pieces. Assume we want to represent this map by an artificial neural network (ANN) using neurons with one hidden layer of neurons having a rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation function. The output layer consists of a single neuron with linear activation function.
How many neurons must the ANN contain at least ?
[math] \( % Generic syms \newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand{\Tt}[0]{\boldsymbol{\theta}} \newcommand{\XX}[0]{{\cal X}} \newcommand{\ZZ}[0]{{\cal Z}} \newcommand{\vx}[0]{{\bf x}} \newcommand{\vv}[0]{{\bf v}} \newcommand{\vu}[0]{{\bf u}} \newcommand{\vs}[0]{{\bf s}} \newcommand{\vm}[0]{{\bf m}} \newcommand{\vq}[0]{{\bf q}} \newcommand{\mX}[0]{{\bf X}} \newcommand{\mC}[0]{{\bf C}} \newcommand{\mA}[0]{{\bf A}} \newcommand{\mL}[0]{{\bf L}} \newcommand{\fscore}[0]{F_{1}} \newcommand{\sparsity}{s} \newcommand{\mW}[0]{{\bf W}} \newcommand{\mD}[0]{{\bf D}} \newcommand{\mZ}[0]{{\bf Z}} \newcommand{\vw}[0]{{\bf w}} \newcommand{\D}[0]{{\mathcal{D}}} \newcommand{\mP}{\mathbf{P}} \newcommand{\mQ}{\mathbf{Q}} \newcommand{\E}[0]{{\mathbb{E}}} \newcommand{\vy}[0]{{\bf y}} \newcommand{\va}[0]{{\bf a}} \newcommand{\vn}[0]{{\bf n}} \newcommand{\vb}[0]{{\bf b}} \newcommand{\vr}[0]{{\bf r}} \newcommand{\vz}[0]{{\bf z}} \newcommand{\N}[0]{{\mathcal{N}}} \newcommand{\vc}[0]{{\bf c}} \newcommand{\bm}{\boldsymbol} % Statistics and Probability Theory \newcommand{\errprob}{p_{\rm err}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{p({#1})} \newcommand{\pdf}[1]{p({#1})} \def \expect {\mathbb{E} } % Machine Learning Symbols \newcommand{\biasterm}{B} \newcommand{\varianceterm}{V} \newcommand{\neighbourhood}[1]{\mathcal{N}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrfolds}{k} \newcommand{\mseesterr}{E_{\rm est}} \newcommand{\bootstrapidx}{b} %\newcommand{\modeldim}{r} \newcommand{\modelidx}{l} \newcommand{\nrbootstraps}{B} \newcommand{\sampleweight}[1]{q^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrcategories}{K} \newcommand{\splitratio}[0]{{\rho}} \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\Vert {#1} \Vert} \newcommand{\sqeuclnorm}[1]{\big\Vert {#1} \big\Vert^{2}_{2}} \newcommand{\bmx}[0]{\begin{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\emx}[0]{\end{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\T}[0]{\text{T}} \DeclareMathOperator*{\rank}{rank} %\newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand\eigvecS{\hat{\mathbf{u}}} \newcommand\eigvecCov{\mathbf{u}} \newcommand\eigvecCoventry{u} \newcommand{\featuredim}{n} \newcommand{\featurelenraw}{\featuredim'} \newcommand{\featurelen}{\featuredim} \newcommand{\samplingset}{\mathcal{M}} \newcommand{\samplesize}{m} \newcommand{\sampleidx}{i} \newcommand{\nractions}{A} \newcommand{\datapoint}{\vz} \newcommand{\actionidx}{a} \newcommand{\clusteridx}{c} \newcommand{\sizehypospace}{D} \newcommand{\nrcluster}{k} \newcommand{\nrseeds}{s} \newcommand{\featureidx}{j} \newcommand{\clustermean}{{\bm \mu}} \newcommand{\clustercov}{{\bm \Sigma}} \newcommand{\target}{y} \newcommand{\error}{E} \newcommand{\augidx}{b} \newcommand{\task}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\nrtasks}{T} \newcommand{\taskidx}{t} \newcommand\truelabel{y} \newcommand{\polydegree}{r} \newcommand\labelvec{\vy} \newcommand\featurevec{\vx} \newcommand\feature{x} \newcommand\predictedlabel{\hat{y}} \newcommand\dataset{\mathcal{D}} \newcommand\trainset{\dataset^{(\rm train)}} \newcommand\valset{\dataset^{(\rm val)}} \newcommand\realcoorspace[1]{\mathbb{R}^{\text{#1}}} \newcommand\effdim[1]{d_{\rm eff} \left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\inspace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\sigmoid}{\sigma} \newcommand{\outspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\hypospace}{\mathcal{H}} \newcommand{\emperror}{\widehat{L}} \newcommand\risk[1]{\expect \big \{ \loss{(\featurevec,\truelabel)}{#1} \big\}} \newcommand{\featurespace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\labelspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\rawfeaturevec}{\mathbf{z}} \newcommand{\rawfeature}{z} \newcommand{\condent}{H} \newcommand{\explanation}{e} \newcommand{\explainset}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\user}{u} \newcommand{\actfun}{\sigma} \newcommand{\noisygrad}{g} \newcommand{\reconstrmap}{r} \newcommand{\predictor}{h} \newcommand{\eigval}[1]{\lambda_{#1}} \newcommand{\regparam}{\lambda} \newcommand{\lrate}{\alpha} \newcommand{\edges}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\generror}{E} \DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp} %\newcommand{\loss}[3]{L({#1},{#2},{#3})} \newcommand{\loss}[2]{L\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\clusterspread}[2]{L^{2}_{\clusteridx}\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\determinant}[1]{{\rm det}({#1})} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\itercntr}{r} \newcommand{\state}{s} \newcommand{\statespace}{\mathcal{S}} \newcommand{\timeidx}{t} \newcommand{\optpolicy}{\pi_{*}} \newcommand{\appoptpolicy}{\hat{\pi}} \newcommand{\dummyidx}{j} \newcommand{\gridsizex}{K} \newcommand{\gridsizey}{L} \newcommand{\localdataset}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\reward}{r} \newcommand{\cumreward}{G} \newcommand{\return}{\cumreward} \newcommand{\action}{a} \newcommand\actionset{\mathcal{A}} \newcommand{\obstacles}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\valuefunc}[1]{v_{#1}} \newcommand{\gridcell}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\pair}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\mdp}[5]{\langle #1, #2, #3, #4, #5 \rangle} \newcommand{\actionvalue}[1]{q_{#1}} \newcommand{\transition}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\policy}{\pi} \newcommand{\charger}{c} \newcommand{\itervar}{k} \newcommand{\discount}{\gamma} \newcommand{\rumba}{Rumba} \newcommand{\actionnorth}{\rm N} \newcommand{\actionsouth}{\rm S} \newcommand{\actioneast}{\rm E} \newcommand{\actionwest}{\rm W} \newcommand{\chargingstations}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\basisfunc}{\phi} \newcommand{\augparam}{B} \newcommand{\valerror}{E_{v}} \newcommand{\trainerror}{E_{t}} \newcommand{\foldidx}{b} \newcommand{\testset}{\dataset^{(\rm test)} } \newcommand{\testerror}{E^{(\rm test)}} \newcommand{\nrmodels}{M} \newcommand{\benchmarkerror}{E^{(\rm ref)}} \newcommand{\lossfun}{L} \newcommand{\datacluster}[1]{\mathcal{C}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\cluster}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\bayeshypothesis}{h^{*}} \newcommand{\featuremtx}{\mX} \newcommand{\weight}{w} \newcommand{\weights}{\vw} \newcommand{\regularizer}{\mathcal{R}} \newcommand{\decreg}[1]{\mathcal{R}_{#1}} \newcommand{\naturalnumbers}{\mathbb{N}} \newcommand{\featuremapvec}{{\bf \Phi}} \newcommand{\featuremap}{\phi} \newcommand{\batchsize}{B} \newcommand{\batch}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\foldsize}{B} \newcommand{\nriter}{R} [/math]
Consider a ANN with [math]\featuredim=10[/math] input neurons following by three hidden layers consisting of [math]4[/math], [math]9[/math] and [math]3[/math] nodes. The three hidden layers are followed by the output layer consisting of a single neuron. Assume that all neurons use a linear activation function and no bias term.
What is the effective dimension [math]\effdim{\hypospace}[/math] of the hypothesis space [math]\hypospace[/math] that consists of all hypothesis maps that can be obtained from this ANN.
[math] \( % Generic syms \newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand{\Tt}[0]{\boldsymbol{\theta}} \newcommand{\XX}[0]{{\cal X}} \newcommand{\ZZ}[0]{{\cal Z}} \newcommand{\vx}[0]{{\bf x}} \newcommand{\vv}[0]{{\bf v}} \newcommand{\vu}[0]{{\bf u}} \newcommand{\vs}[0]{{\bf s}} \newcommand{\vm}[0]{{\bf m}} \newcommand{\vq}[0]{{\bf q}} \newcommand{\mX}[0]{{\bf X}} \newcommand{\mC}[0]{{\bf C}} \newcommand{\mA}[0]{{\bf A}} \newcommand{\mL}[0]{{\bf L}} \newcommand{\fscore}[0]{F_{1}} \newcommand{\sparsity}{s} \newcommand{\mW}[0]{{\bf W}} \newcommand{\mD}[0]{{\bf D}} \newcommand{\mZ}[0]{{\bf Z}} \newcommand{\vw}[0]{{\bf w}} \newcommand{\D}[0]{{\mathcal{D}}} \newcommand{\mP}{\mathbf{P}} \newcommand{\mQ}{\mathbf{Q}} \newcommand{\E}[0]{{\mathbb{E}}} \newcommand{\vy}[0]{{\bf y}} \newcommand{\va}[0]{{\bf a}} \newcommand{\vn}[0]{{\bf n}} \newcommand{\vb}[0]{{\bf b}} \newcommand{\vr}[0]{{\bf r}} \newcommand{\vz}[0]{{\bf z}} \newcommand{\N}[0]{{\mathcal{N}}} \newcommand{\vc}[0]{{\bf c}} \newcommand{\bm}{\boldsymbol} % Statistics and Probability Theory \newcommand{\errprob}{p_{\rm err}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{p({#1})} \newcommand{\pdf}[1]{p({#1})} \def \expect {\mathbb{E} } % Machine Learning Symbols \newcommand{\biasterm}{B} \newcommand{\varianceterm}{V} \newcommand{\neighbourhood}[1]{\mathcal{N}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrfolds}{k} \newcommand{\mseesterr}{E_{\rm est}} \newcommand{\bootstrapidx}{b} %\newcommand{\modeldim}{r} \newcommand{\modelidx}{l} \newcommand{\nrbootstraps}{B} \newcommand{\sampleweight}[1]{q^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrcategories}{K} \newcommand{\splitratio}[0]{{\rho}} \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\Vert {#1} \Vert} \newcommand{\sqeuclnorm}[1]{\big\Vert {#1} \big\Vert^{2}_{2}} \newcommand{\bmx}[0]{\begin{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\emx}[0]{\end{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\T}[0]{\text{T}} \DeclareMathOperator*{\rank}{rank} %\newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand\eigvecS{\hat{\mathbf{u}}} \newcommand\eigvecCov{\mathbf{u}} \newcommand\eigvecCoventry{u} \newcommand{\featuredim}{n} \newcommand{\featurelenraw}{\featuredim'} \newcommand{\featurelen}{\featuredim} \newcommand{\samplingset}{\mathcal{M}} \newcommand{\samplesize}{m} \newcommand{\sampleidx}{i} \newcommand{\nractions}{A} \newcommand{\datapoint}{\vz} \newcommand{\actionidx}{a} \newcommand{\clusteridx}{c} \newcommand{\sizehypospace}{D} \newcommand{\nrcluster}{k} \newcommand{\nrseeds}{s} \newcommand{\featureidx}{j} \newcommand{\clustermean}{{\bm \mu}} \newcommand{\clustercov}{{\bm \Sigma}} \newcommand{\target}{y} \newcommand{\error}{E} \newcommand{\augidx}{b} \newcommand{\task}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\nrtasks}{T} \newcommand{\taskidx}{t} \newcommand\truelabel{y} \newcommand{\polydegree}{r} \newcommand\labelvec{\vy} \newcommand\featurevec{\vx} \newcommand\feature{x} \newcommand\predictedlabel{\hat{y}} \newcommand\dataset{\mathcal{D}} \newcommand\trainset{\dataset^{(\rm train)}} \newcommand\valset{\dataset^{(\rm val)}} \newcommand\realcoorspace[1]{\mathbb{R}^{\text{#1}}} \newcommand\effdim[1]{d_{\rm eff} \left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\inspace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\sigmoid}{\sigma} \newcommand{\outspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\hypospace}{\mathcal{H}} \newcommand{\emperror}{\widehat{L}} \newcommand\risk[1]{\expect \big \{ \loss{(\featurevec,\truelabel)}{#1} \big\}} \newcommand{\featurespace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\labelspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\rawfeaturevec}{\mathbf{z}} \newcommand{\rawfeature}{z} \newcommand{\condent}{H} \newcommand{\explanation}{e} \newcommand{\explainset}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\user}{u} \newcommand{\actfun}{\sigma} \newcommand{\noisygrad}{g} \newcommand{\reconstrmap}{r} \newcommand{\predictor}{h} \newcommand{\eigval}[1]{\lambda_{#1}} \newcommand{\regparam}{\lambda} \newcommand{\lrate}{\alpha} \newcommand{\edges}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\generror}{E} \DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp} %\newcommand{\loss}[3]{L({#1},{#2},{#3})} \newcommand{\loss}[2]{L\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\clusterspread}[2]{L^{2}_{\clusteridx}\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\determinant}[1]{{\rm det}({#1})} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\itercntr}{r} \newcommand{\state}{s} \newcommand{\statespace}{\mathcal{S}} \newcommand{\timeidx}{t} \newcommand{\optpolicy}{\pi_{*}} \newcommand{\appoptpolicy}{\hat{\pi}} \newcommand{\dummyidx}{j} \newcommand{\gridsizex}{K} \newcommand{\gridsizey}{L} \newcommand{\localdataset}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\reward}{r} \newcommand{\cumreward}{G} \newcommand{\return}{\cumreward} \newcommand{\action}{a} \newcommand\actionset{\mathcal{A}} \newcommand{\obstacles}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\valuefunc}[1]{v_{#1}} \newcommand{\gridcell}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\pair}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\mdp}[5]{\langle #1, #2, #3, #4, #5 \rangle} \newcommand{\actionvalue}[1]{q_{#1}} \newcommand{\transition}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\policy}{\pi} \newcommand{\charger}{c} \newcommand{\itervar}{k} \newcommand{\discount}{\gamma} \newcommand{\rumba}{Rumba} \newcommand{\actionnorth}{\rm N} \newcommand{\actionsouth}{\rm S} \newcommand{\actioneast}{\rm E} \newcommand{\actionwest}{\rm W} \newcommand{\chargingstations}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\basisfunc}{\phi} \newcommand{\augparam}{B} \newcommand{\valerror}{E_{v}} \newcommand{\trainerror}{E_{t}} \newcommand{\foldidx}{b} \newcommand{\testset}{\dataset^{(\rm test)} } \newcommand{\testerror}{E^{(\rm test)}} \newcommand{\nrmodels}{M} \newcommand{\benchmarkerror}{E^{(\rm ref)}} \newcommand{\lossfun}{L} \newcommand{\datacluster}[1]{\mathcal{C}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\cluster}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\bayeshypothesis}{h^{*}} \newcommand{\featuremtx}{\mX} \newcommand{\weight}{w} \newcommand{\weights}{\vw} \newcommand{\regularizer}{\mathcal{R}} \newcommand{\decreg}[1]{\mathcal{R}_{#1}} \newcommand{\naturalnumbers}{\mathbb{N}} \newcommand{\featuremapvec}{{\bf \Phi}} \newcommand{\featuremap}{\phi} \newcommand{\batchsize}{B} \newcommand{\batch}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\foldsize}{B} \newcommand{\nriter}{R} [/math]
Consider data points characterized by feature vectors [math]\featurevec \in \mathbb{R}^{\featuredim}[/math] and binary labels [math]\truelabel \in\{-1,1\}[/math].
We are interested in finding a good linear classifier which is such that the feature vectors resulting in [math]h(\featurevec) = 1[/math] is a half-space.
Which of the methods discussed in this chapter aim at learning a linear classifier?
[math] % Generic syms \newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand{\Tt}[0]{\boldsymbol{\theta}} \newcommand{\XX}[0]{{\cal X}} \newcommand{\ZZ}[0]{{\cal Z}} \newcommand{\vx}[0]{{\bf x}} \newcommand{\vv}[0]{{\bf v}} \newcommand{\vu}[0]{{\bf u}} \newcommand{\vs}[0]{{\bf s}} \newcommand{\vm}[0]{{\bf m}} \newcommand{\vq}[0]{{\bf q}} \newcommand{\mX}[0]{{\bf X}} \newcommand{\mC}[0]{{\bf C}} \newcommand{\mA}[0]{{\bf A}} \newcommand{\mL}[0]{{\bf L}} \newcommand{\fscore}[0]{F_{1}} \newcommand{\sparsity}{s} \newcommand{\mW}[0]{{\bf W}} \newcommand{\mD}[0]{{\bf D}} \newcommand{\mZ}[0]{{\bf Z}} \newcommand{\vw}[0]{{\bf w}} \newcommand{\D}[0]{{\mathcal{D}}} \newcommand{\mP}{\mathbf{P}} \newcommand{\mQ}{\mathbf{Q}} \newcommand{\E}[0]{{\mathbb{E}}} \newcommand{\vy}[0]{{\bf y}} \newcommand{\va}[0]{{\bf a}} \newcommand{\vn}[0]{{\bf n}} \newcommand{\vb}[0]{{\bf b}} \newcommand{\vr}[0]{{\bf r}} \newcommand{\vz}[0]{{\bf z}} \newcommand{\N}[0]{{\mathcal{N}}} \newcommand{\vc}[0]{{\bf c}} \newcommand{\bm}{\boldsymbol} % Statistics and Probability Theory \newcommand{\errprob}{p_{\rm err}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{p({#1})} \newcommand{\pdf}[1]{p({#1})} \def \expect {\mathbb{E} } % Machine Learning Symbols \newcommand{\biasterm}{B} \newcommand{\varianceterm}{V} \newcommand{\neighbourhood}[1]{\mathcal{N}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrfolds}{k} \newcommand{\mseesterr}{E_{\rm est}} \newcommand{\bootstrapidx}{b} %\newcommand{\modeldim}{r} \newcommand{\modelidx}{l} \newcommand{\nrbootstraps}{B} \newcommand{\sampleweight}[1]{q^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrcategories}{K} \newcommand{\splitratio}[0]{{\rho}} \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\Vert {#1} \Vert} \newcommand{\sqeuclnorm}[1]{\big\Vert {#1} \big\Vert^{2}_{2}} \newcommand{\bmx}[0]{\begin{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\emx}[0]{\end{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\T}[0]{\text{T}} \DeclareMathOperator*{\rank}{rank} %\newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand\eigvecS{\hat{\mathbf{u}}} \newcommand\eigvecCov{\mathbf{u}} \newcommand\eigvecCoventry{u} \newcommand{\featuredim}{n} \newcommand{\featurelenraw}{\featuredim'} \newcommand{\featurelen}{\featuredim} \newcommand{\samplingset}{\mathcal{M}} \newcommand{\samplesize}{m} \newcommand{\sampleidx}{i} \newcommand{\nractions}{A} \newcommand{\datapoint}{\vz} \newcommand{\actionidx}{a} \newcommand{\clusteridx}{c} \newcommand{\sizehypospace}{D} \newcommand{\nrcluster}{k} \newcommand{\nrseeds}{s} \newcommand{\featureidx}{j} \newcommand{\clustermean}{{\bm \mu}} \newcommand{\clustercov}{{\bm \Sigma}} \newcommand{\target}{y} \newcommand{\error}{E} \newcommand{\augidx}{b} \newcommand{\task}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\nrtasks}{T} \newcommand{\taskidx}{t} \newcommand\truelabel{y} \newcommand{\polydegree}{r} \newcommand\labelvec{\vy} \newcommand\featurevec{\vx} \newcommand\feature{x} \newcommand\predictedlabel{\hat{y}} \newcommand\dataset{\mathcal{D}} \newcommand\trainset{\dataset^{(\rm train)}} \newcommand\valset{\dataset^{(\rm val)}} \newcommand\realcoorspace[1]{\mathbb{R}^{\text{#1}}} \newcommand\effdim[1]{d_{\rm eff} \left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\inspace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\sigmoid}{\sigma} \newcommand{\outspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\hypospace}{\mathcal{H}} \newcommand{\emperror}{\widehat{L}} \newcommand\risk[1]{\expect \big \{ \loss{(\featurevec,\truelabel)}{#1} \big\}} \newcommand{\featurespace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\labelspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\rawfeaturevec}{\mathbf{z}} \newcommand{\rawfeature}{z} \newcommand{\condent}{H} \newcommand{\explanation}{e} \newcommand{\explainset}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\user}{u} \newcommand{\actfun}{\sigma} \newcommand{\noisygrad}{g} \newcommand{\reconstrmap}{r} \newcommand{\predictor}{h} \newcommand{\eigval}[1]{\lambda_{#1}} \newcommand{\regparam}{\lambda} \newcommand{\lrate}{\alpha} \newcommand{\edges}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\generror}{E} \DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp} %\newcommand{\loss}[3]{L({#1},{#2},{#3})} \newcommand{\loss}[2]{L\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\clusterspread}[2]{L^{2}_{\clusteridx}\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\determinant}[1]{{\rm det}({#1})} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\itercntr}{r} \newcommand{\state}{s} \newcommand{\statespace}{\mathcal{S}} \newcommand{\timeidx}{t} \newcommand{\optpolicy}{\pi_{*}} \newcommand{\appoptpolicy}{\hat{\pi}} \newcommand{\dummyidx}{j} \newcommand{\gridsizex}{K} \newcommand{\gridsizey}{L} \newcommand{\localdataset}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\reward}{r} \newcommand{\cumreward}{G} \newcommand{\return}{\cumreward} \newcommand{\action}{a} \newcommand\actionset{\mathcal{A}} \newcommand{\obstacles}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\valuefunc}[1]{v_{#1}} \newcommand{\gridcell}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\pair}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\mdp}[5]{\langle #1, #2, #3, #4, #5 \rangle} \newcommand{\actionvalue}[1]{q_{#1}} \newcommand{\transition}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\policy}{\pi} \newcommand{\charger}{c} \newcommand{\itervar}{k} \newcommand{\discount}{\gamma} \newcommand{\rumba}{Rumba} \newcommand{\actionnorth}{\rm N} \newcommand{\actionsouth}{\rm S} \newcommand{\actioneast}{\rm E} \newcommand{\actionwest}{\rm W} \newcommand{\chargingstations}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\basisfunc}{\phi} \newcommand{\augparam}{B} \newcommand{\valerror}{E_{v}} \newcommand{\trainerror}{E_{t}} \newcommand{\foldidx}{b} \newcommand{\testset}{\dataset^{(\rm test)} } \newcommand{\testerror}{E^{(\rm test)}} \newcommand{\nrmodels}{M} \newcommand{\benchmarkerror}{E^{(\rm ref)}} \newcommand{\lossfun}{L} \newcommand{\datacluster}[1]{\mathcal{C}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\cluster}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\bayeshypothesis}{h^{*}} \newcommand{\featuremtx}{\mX} \newcommand{\weight}{w} \newcommand{\weights}{\vw} \newcommand{\regularizer}{\mathcal{R}} \newcommand{\decreg}[1]{\mathcal{R}_{#1}} \newcommand{\naturalnumbers}{\mathbb{N}} \newcommand{\featuremapvec}{{\bf \Phi}} \newcommand{\featuremap}{\phi} \newcommand{\batchsize}{B} \newcommand{\batch}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\foldsize}{B} \newcommand{\nriter}{R} [/math]
Consider a ML application involving data points with features [math]\featurevec \in \mathbb{R}^{6}[/math] and a numeric label [math]\truelabel \in \mathbb{R}[/math]. We learn a hypothesis by minimizing the average loss incurred on a training set [math]\dataset = \big\{\big(\featurevec^{(1)},\truelabel^{(1)}\big),\ldots,\big(\featurevec^{(\samplesize)},\truelabel^{(\samplesize)}\big)\big\}[/math].
Which of the following ML methods uses a hypothesis space that depends on the dataset [math]\dataset[/math]?
[math] % Generic syms \newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand{\Tt}[0]{\boldsymbol{\theta}} \newcommand{\XX}[0]{{\cal X}} \newcommand{\ZZ}[0]{{\cal Z}} \newcommand{\vx}[0]{{\bf x}} \newcommand{\vv}[0]{{\bf v}} \newcommand{\vu}[0]{{\bf u}} \newcommand{\vs}[0]{{\bf s}} \newcommand{\vm}[0]{{\bf m}} \newcommand{\vq}[0]{{\bf q}} \newcommand{\mX}[0]{{\bf X}} \newcommand{\mC}[0]{{\bf C}} \newcommand{\mA}[0]{{\bf A}} \newcommand{\mL}[0]{{\bf L}} \newcommand{\fscore}[0]{F_{1}} \newcommand{\sparsity}{s} \newcommand{\mW}[0]{{\bf W}} \newcommand{\mD}[0]{{\bf D}} \newcommand{\mZ}[0]{{\bf Z}} \newcommand{\vw}[0]{{\bf w}} \newcommand{\D}[0]{{\mathcal{D}}} \newcommand{\mP}{\mathbf{P}} \newcommand{\mQ}{\mathbf{Q}} \newcommand{\E}[0]{{\mathbb{E}}} \newcommand{\vy}[0]{{\bf y}} \newcommand{\va}[0]{{\bf a}} \newcommand{\vn}[0]{{\bf n}} \newcommand{\vb}[0]{{\bf b}} \newcommand{\vr}[0]{{\bf r}} \newcommand{\vz}[0]{{\bf z}} \newcommand{\N}[0]{{\mathcal{N}}} \newcommand{\vc}[0]{{\bf c}} \newcommand{\bm}{\boldsymbol} % Statistics and Probability Theory \newcommand{\errprob}{p_{\rm err}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{p({#1})} \newcommand{\pdf}[1]{p({#1})} \def \expect {\mathbb{E} } % Machine Learning Symbols \newcommand{\biasterm}{B} \newcommand{\varianceterm}{V} \newcommand{\neighbourhood}[1]{\mathcal{N}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrfolds}{k} \newcommand{\mseesterr}{E_{\rm est}} \newcommand{\bootstrapidx}{b} %\newcommand{\modeldim}{r} \newcommand{\modelidx}{l} \newcommand{\nrbootstraps}{B} \newcommand{\sampleweight}[1]{q^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrcategories}{K} \newcommand{\splitratio}[0]{{\rho}} \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\Vert {#1} \Vert} \newcommand{\sqeuclnorm}[1]{\big\Vert {#1} \big\Vert^{2}_{2}} \newcommand{\bmx}[0]{\begin{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\emx}[0]{\end{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\T}[0]{\text{T}} \DeclareMathOperator*{\rank}{rank} %\newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand\eigvecS{\hat{\mathbf{u}}} \newcommand\eigvecCov{\mathbf{u}} \newcommand\eigvecCoventry{u} \newcommand{\featuredim}{n} \newcommand{\featurelenraw}{\featuredim'} \newcommand{\featurelen}{\featuredim} \newcommand{\samplingset}{\mathcal{M}} \newcommand{\samplesize}{m} \newcommand{\sampleidx}{i} \newcommand{\nractions}{A} \newcommand{\datapoint}{\vz} \newcommand{\actionidx}{a} \newcommand{\clusteridx}{c} \newcommand{\sizehypospace}{D} \newcommand{\nrcluster}{k} \newcommand{\nrseeds}{s} \newcommand{\featureidx}{j} \newcommand{\clustermean}{{\bm \mu}} \newcommand{\clustercov}{{\bm \Sigma}} \newcommand{\target}{y} \newcommand{\error}{E} \newcommand{\augidx}{b} \newcommand{\task}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\nrtasks}{T} \newcommand{\taskidx}{t} \newcommand\truelabel{y} \newcommand{\polydegree}{r} \newcommand\labelvec{\vy} \newcommand\featurevec{\vx} \newcommand\feature{x} \newcommand\predictedlabel{\hat{y}} \newcommand\dataset{\mathcal{D}} \newcommand\trainset{\dataset^{(\rm train)}} \newcommand\valset{\dataset^{(\rm val)}} \newcommand\realcoorspace[1]{\mathbb{R}^{\text{#1}}} \newcommand\effdim[1]{d_{\rm eff} \left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\inspace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\sigmoid}{\sigma} \newcommand{\outspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\hypospace}{\mathcal{H}} \newcommand{\emperror}{\widehat{L}} \newcommand\risk[1]{\expect \big \{ \loss{(\featurevec,\truelabel)}{#1} \big\}} \newcommand{\featurespace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\labelspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\rawfeaturevec}{\mathbf{z}} \newcommand{\rawfeature}{z} \newcommand{\condent}{H} \newcommand{\explanation}{e} \newcommand{\explainset}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\user}{u} \newcommand{\actfun}{\sigma} \newcommand{\noisygrad}{g} \newcommand{\reconstrmap}{r} \newcommand{\predictor}{h} \newcommand{\eigval}[1]{\lambda_{#1}} \newcommand{\regparam}{\lambda} \newcommand{\lrate}{\alpha} \newcommand{\edges}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\generror}{E} \DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp} %\newcommand{\loss}[3]{L({#1},{#2},{#3})} \newcommand{\loss}[2]{L\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\clusterspread}[2]{L^{2}_{\clusteridx}\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\determinant}[1]{{\rm det}({#1})} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\itercntr}{r} \newcommand{\state}{s} \newcommand{\statespace}{\mathcal{S}} \newcommand{\timeidx}{t} \newcommand{\optpolicy}{\pi_{*}} \newcommand{\appoptpolicy}{\hat{\pi}} \newcommand{\dummyidx}{j} \newcommand{\gridsizex}{K} \newcommand{\gridsizey}{L} \newcommand{\localdataset}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\reward}{r} \newcommand{\cumreward}{G} \newcommand{\return}{\cumreward} \newcommand{\action}{a} \newcommand\actionset{\mathcal{A}} \newcommand{\obstacles}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\valuefunc}[1]{v_{#1}} \newcommand{\gridcell}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\pair}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\mdp}[5]{\langle #1, #2, #3, #4, #5 \rangle} \newcommand{\actionvalue}[1]{q_{#1}} \newcommand{\transition}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\policy}{\pi} \newcommand{\charger}{c} \newcommand{\itervar}{k} \newcommand{\discount}{\gamma} \newcommand{\rumba}{Rumba} \newcommand{\actionnorth}{\rm N} \newcommand{\actionsouth}{\rm S} \newcommand{\actioneast}{\rm E} \newcommand{\actionwest}{\rm W} \newcommand{\chargingstations}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\basisfunc}{\phi} \newcommand{\augparam}{B} \newcommand{\valerror}{E_{v}} \newcommand{\trainerror}{E_{t}} \newcommand{\foldidx}{b} \newcommand{\testset}{\dataset^{(\rm test)} } \newcommand{\testerror}{E^{(\rm test)}} \newcommand{\nrmodels}{M} \newcommand{\benchmarkerror}{E^{(\rm ref)}} \newcommand{\lossfun}{L} \newcommand{\datacluster}[1]{\mathcal{C}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\cluster}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\bayeshypothesis}{h^{*}} \newcommand{\featuremtx}{\mX} \newcommand{\weight}{w} \newcommand{\weights}{\vw} \newcommand{\regularizer}{\mathcal{R}} \newcommand{\decreg}[1]{\mathcal{R}_{#1}} \newcommand{\naturalnumbers}{\mathbb{N}} \newcommand{\featuremapvec}{{\bf \Phi}} \newcommand{\featuremap}{\phi} \newcommand{\batchsize}{B} \newcommand{\batch}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\foldsize}{B} \newcommand{\nriter}{R} [/math]
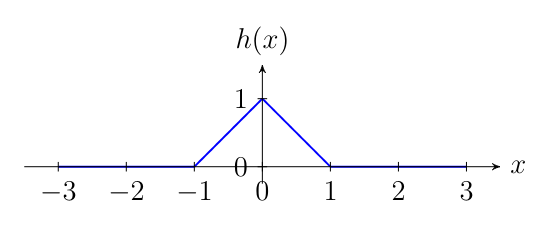
Consider the ANN in Figure fig_ANN using the ReLU activation function (see Figure fig_activate_neuron).
Show that there is a particular choice for the weights [math]\weights =(\weight_{1},\ldots,\weight_{9})^{T}[/math] such that the resulting hypothesis map [math]h^{(\weights)}(\feature)[/math] is a triangle as depicted in the figure below.
Can you also find a choice for the weights [math]\weights =(\weight_{1},\ldots,\weight_{9})^{T}[/math] that produce the same triangle shape if we replace the ReLU activation function with the linear function [math]\actfun(z) =10 \cdot z[/math]?
[math] \( % Generic syms \newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand{\Tt}[0]{\boldsymbol{\theta}} \newcommand{\XX}[0]{{\cal X}} \newcommand{\ZZ}[0]{{\cal Z}} \newcommand{\vx}[0]{{\bf x}} \newcommand{\vv}[0]{{\bf v}} \newcommand{\vu}[0]{{\bf u}} \newcommand{\vs}[0]{{\bf s}} \newcommand{\vm}[0]{{\bf m}} \newcommand{\vq}[0]{{\bf q}} \newcommand{\mX}[0]{{\bf X}} \newcommand{\mC}[0]{{\bf C}} \newcommand{\mA}[0]{{\bf A}} \newcommand{\mL}[0]{{\bf L}} \newcommand{\fscore}[0]{F_{1}} \newcommand{\sparsity}{s} \newcommand{\mW}[0]{{\bf W}} \newcommand{\mD}[0]{{\bf D}} \newcommand{\mZ}[0]{{\bf Z}} \newcommand{\vw}[0]{{\bf w}} \newcommand{\D}[0]{{\mathcal{D}}} \newcommand{\mP}{\mathbf{P}} \newcommand{\mQ}{\mathbf{Q}} \newcommand{\E}[0]{{\mathbb{E}}} \newcommand{\vy}[0]{{\bf y}} \newcommand{\va}[0]{{\bf a}} \newcommand{\vn}[0]{{\bf n}} \newcommand{\vb}[0]{{\bf b}} \newcommand{\vr}[0]{{\bf r}} \newcommand{\vz}[0]{{\bf z}} \newcommand{\N}[0]{{\mathcal{N}}} \newcommand{\vc}[0]{{\bf c}} \newcommand{\bm}{\boldsymbol} % Statistics and Probability Theory \newcommand{\errprob}{p_{\rm err}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{p({#1})} \newcommand{\pdf}[1]{p({#1})} \def \expect {\mathbb{E} } % Machine Learning Symbols \newcommand{\biasterm}{B} \newcommand{\varianceterm}{V} \newcommand{\neighbourhood}[1]{\mathcal{N}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrfolds}{k} \newcommand{\mseesterr}{E_{\rm est}} \newcommand{\bootstrapidx}{b} %\newcommand{\modeldim}{r} \newcommand{\modelidx}{l} \newcommand{\nrbootstraps}{B} \newcommand{\sampleweight}[1]{q^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrcategories}{K} \newcommand{\splitratio}[0]{{\rho}} \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\Vert {#1} \Vert} \newcommand{\sqeuclnorm}[1]{\big\Vert {#1} \big\Vert^{2}_{2}} \newcommand{\bmx}[0]{\begin{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\emx}[0]{\end{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\T}[0]{\text{T}} \DeclareMathOperator*{\rank}{rank} %\newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand\eigvecS{\hat{\mathbf{u}}} \newcommand\eigvecCov{\mathbf{u}} \newcommand\eigvecCoventry{u} \newcommand{\featuredim}{n} \newcommand{\featurelenraw}{\featuredim'} \newcommand{\featurelen}{\featuredim} \newcommand{\samplingset}{\mathcal{M}} \newcommand{\samplesize}{m} \newcommand{\sampleidx}{i} \newcommand{\nractions}{A} \newcommand{\datapoint}{\vz} \newcommand{\actionidx}{a} \newcommand{\clusteridx}{c} \newcommand{\sizehypospace}{D} \newcommand{\nrcluster}{k} \newcommand{\nrseeds}{s} \newcommand{\featureidx}{j} \newcommand{\clustermean}{{\bm \mu}} \newcommand{\clustercov}{{\bm \Sigma}} \newcommand{\target}{y} \newcommand{\error}{E} \newcommand{\augidx}{b} \newcommand{\task}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\nrtasks}{T} \newcommand{\taskidx}{t} \newcommand\truelabel{y} \newcommand{\polydegree}{r} \newcommand\labelvec{\vy} \newcommand\featurevec{\vx} \newcommand\feature{x} \newcommand\predictedlabel{\hat{y}} \newcommand\dataset{\mathcal{D}} \newcommand\trainset{\dataset^{(\rm train)}} \newcommand\valset{\dataset^{(\rm val)}} \newcommand\realcoorspace[1]{\mathbb{R}^{\text{#1}}} \newcommand\effdim[1]{d_{\rm eff} \left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\inspace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\sigmoid}{\sigma} \newcommand{\outspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\hypospace}{\mathcal{H}} \newcommand{\emperror}{\widehat{L}} \newcommand\risk[1]{\expect \big \{ \loss{(\featurevec,\truelabel)}{#1} \big\}} \newcommand{\featurespace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\labelspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\rawfeaturevec}{\mathbf{z}} \newcommand{\rawfeature}{z} \newcommand{\condent}{H} \newcommand{\explanation}{e} \newcommand{\explainset}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\user}{u} \newcommand{\actfun}{\sigma} \newcommand{\noisygrad}{g} \newcommand{\reconstrmap}{r} \newcommand{\predictor}{h} \newcommand{\eigval}[1]{\lambda_{#1}} \newcommand{\regparam}{\lambda} \newcommand{\lrate}{\alpha} \newcommand{\edges}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\generror}{E} \DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp} %\newcommand{\loss}[3]{L({#1},{#2},{#3})} \newcommand{\loss}[2]{L\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\clusterspread}[2]{L^{2}_{\clusteridx}\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\determinant}[1]{{\rm det}({#1})} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\itercntr}{r} \newcommand{\state}{s} \newcommand{\statespace}{\mathcal{S}} \newcommand{\timeidx}{t} \newcommand{\optpolicy}{\pi_{*}} \newcommand{\appoptpolicy}{\hat{\pi}} \newcommand{\dummyidx}{j} \newcommand{\gridsizex}{K} \newcommand{\gridsizey}{L} \newcommand{\localdataset}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\reward}{r} \newcommand{\cumreward}{G} \newcommand{\return}{\cumreward} \newcommand{\action}{a} \newcommand\actionset{\mathcal{A}} \newcommand{\obstacles}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\valuefunc}[1]{v_{#1}} \newcommand{\gridcell}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\pair}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\mdp}[5]{\langle #1, #2, #3, #4, #5 \rangle} \newcommand{\actionvalue}[1]{q_{#1}} \newcommand{\transition}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\policy}{\pi} \newcommand{\charger}{c} \newcommand{\itervar}{k} \newcommand{\discount}{\gamma} \newcommand{\rumba}{Rumba} \newcommand{\actionnorth}{\rm N} \newcommand{\actionsouth}{\rm S} \newcommand{\actioneast}{\rm E} \newcommand{\actionwest}{\rm W} \newcommand{\chargingstations}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\basisfunc}{\phi} \newcommand{\augparam}{B} \newcommand{\valerror}{E_{v}} \newcommand{\trainerror}{E_{t}} \newcommand{\foldidx}{b} \newcommand{\testset}{\dataset^{(\rm test)} } \newcommand{\testerror}{E^{(\rm test)}} \newcommand{\nrmodels}{M} \newcommand{\benchmarkerror}{E^{(\rm ref)}} \newcommand{\lossfun}{L} \newcommand{\datacluster}[1]{\mathcal{C}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\cluster}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\bayeshypothesis}{h^{*}} \newcommand{\featuremtx}{\mX} \newcommand{\weight}{w} \newcommand{\weights}{\vw} \newcommand{\regularizer}{\mathcal{R}} \newcommand{\decreg}[1]{\mathcal{R}_{#1}} \newcommand{\naturalnumbers}{\mathbb{N}} \newcommand{\featuremapvec}{{\bf \Phi}} \newcommand{\featuremap}{\phi} \newcommand{\batchsize}{B} \newcommand{\batch}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\foldsize}{B} \newcommand{\nriter}{R} [/math]
Try to approximate the hypothesis map depicted in the figure below by an element of [math]\hypospace_{\rm Gauss}[/math] (see equ_def_Gauss_hypospace) using [math]\sigma=1/10[/math], [math]\featuredim=10[/math] and [math]\mu_{\featureidx} = -1 + (2\featureidx/10)[/math].
[math] \( % Generic syms \newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand{\Tt}[0]{\boldsymbol{\theta}} \newcommand{\XX}[0]{{\cal X}} \newcommand{\ZZ}[0]{{\cal Z}} \newcommand{\vx}[0]{{\bf x}} \newcommand{\vv}[0]{{\bf v}} \newcommand{\vu}[0]{{\bf u}} \newcommand{\vs}[0]{{\bf s}} \newcommand{\vm}[0]{{\bf m}} \newcommand{\vq}[0]{{\bf q}} \newcommand{\mX}[0]{{\bf X}} \newcommand{\mC}[0]{{\bf C}} \newcommand{\mA}[0]{{\bf A}} \newcommand{\mL}[0]{{\bf L}} \newcommand{\fscore}[0]{F_{1}} \newcommand{\sparsity}{s} \newcommand{\mW}[0]{{\bf W}} \newcommand{\mD}[0]{{\bf D}} \newcommand{\mZ}[0]{{\bf Z}} \newcommand{\vw}[0]{{\bf w}} \newcommand{\D}[0]{{\mathcal{D}}} \newcommand{\mP}{\mathbf{P}} \newcommand{\mQ}{\mathbf{Q}} \newcommand{\E}[0]{{\mathbb{E}}} \newcommand{\vy}[0]{{\bf y}} \newcommand{\va}[0]{{\bf a}} \newcommand{\vn}[0]{{\bf n}} \newcommand{\vb}[0]{{\bf b}} \newcommand{\vr}[0]{{\bf r}} \newcommand{\vz}[0]{{\bf z}} \newcommand{\N}[0]{{\mathcal{N}}} \newcommand{\vc}[0]{{\bf c}} \newcommand{\bm}{\boldsymbol} % Statistics and Probability Theory \newcommand{\errprob}{p_{\rm err}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{p({#1})} \newcommand{\pdf}[1]{p({#1})} \def \expect {\mathbb{E} } % Machine Learning Symbols \newcommand{\biasterm}{B} \newcommand{\varianceterm}{V} \newcommand{\neighbourhood}[1]{\mathcal{N}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrfolds}{k} \newcommand{\mseesterr}{E_{\rm est}} \newcommand{\bootstrapidx}{b} %\newcommand{\modeldim}{r} \newcommand{\modelidx}{l} \newcommand{\nrbootstraps}{B} \newcommand{\sampleweight}[1]{q^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrcategories}{K} \newcommand{\splitratio}[0]{{\rho}} \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\Vert {#1} \Vert} \newcommand{\sqeuclnorm}[1]{\big\Vert {#1} \big\Vert^{2}_{2}} \newcommand{\bmx}[0]{\begin{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\emx}[0]{\end{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\T}[0]{\text{T}} \DeclareMathOperator*{\rank}{rank} %\newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand\eigvecS{\hat{\mathbf{u}}} \newcommand\eigvecCov{\mathbf{u}} \newcommand\eigvecCoventry{u} \newcommand{\featuredim}{n} \newcommand{\featurelenraw}{\featuredim'} \newcommand{\featurelen}{\featuredim} \newcommand{\samplingset}{\mathcal{M}} \newcommand{\samplesize}{m} \newcommand{\sampleidx}{i} \newcommand{\nractions}{A} \newcommand{\datapoint}{\vz} \newcommand{\actionidx}{a} \newcommand{\clusteridx}{c} \newcommand{\sizehypospace}{D} \newcommand{\nrcluster}{k} \newcommand{\nrseeds}{s} \newcommand{\featureidx}{j} \newcommand{\clustermean}{{\bm \mu}} \newcommand{\clustercov}{{\bm \Sigma}} \newcommand{\target}{y} \newcommand{\error}{E} \newcommand{\augidx}{b} \newcommand{\task}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\nrtasks}{T} \newcommand{\taskidx}{t} \newcommand\truelabel{y} \newcommand{\polydegree}{r} \newcommand\labelvec{\vy} \newcommand\featurevec{\vx} \newcommand\feature{x} \newcommand\predictedlabel{\hat{y}} \newcommand\dataset{\mathcal{D}} \newcommand\trainset{\dataset^{(\rm train)}} \newcommand\valset{\dataset^{(\rm val)}} \newcommand\realcoorspace[1]{\mathbb{R}^{\text{#1}}} \newcommand\effdim[1]{d_{\rm eff} \left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\inspace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\sigmoid}{\sigma} \newcommand{\outspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\hypospace}{\mathcal{H}} \newcommand{\emperror}{\widehat{L}} \newcommand\risk[1]{\expect \big \{ \loss{(\featurevec,\truelabel)}{#1} \big\}} \newcommand{\featurespace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\labelspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\rawfeaturevec}{\mathbf{z}} \newcommand{\rawfeature}{z} \newcommand{\condent}{H} \newcommand{\explanation}{e} \newcommand{\explainset}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\user}{u} \newcommand{\actfun}{\sigma} \newcommand{\noisygrad}{g} \newcommand{\reconstrmap}{r} \newcommand{\predictor}{h} \newcommand{\eigval}[1]{\lambda_{#1}} \newcommand{\regparam}{\lambda} \newcommand{\lrate}{\alpha} \newcommand{\edges}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\generror}{E} \DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp} %\newcommand{\loss}[3]{L({#1},{#2},{#3})} \newcommand{\loss}[2]{L\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\clusterspread}[2]{L^{2}_{\clusteridx}\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\determinant}[1]{{\rm det}({#1})} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\itercntr}{r} \newcommand{\state}{s} \newcommand{\statespace}{\mathcal{S}} \newcommand{\timeidx}{t} \newcommand{\optpolicy}{\pi_{*}} \newcommand{\appoptpolicy}{\hat{\pi}} \newcommand{\dummyidx}{j} \newcommand{\gridsizex}{K} \newcommand{\gridsizey}{L} \newcommand{\localdataset}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\reward}{r} \newcommand{\cumreward}{G} \newcommand{\return}{\cumreward} \newcommand{\action}{a} \newcommand\actionset{\mathcal{A}} \newcommand{\obstacles}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\valuefunc}[1]{v_{#1}} \newcommand{\gridcell}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\pair}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\mdp}[5]{\langle #1, #2, #3, #4, #5 \rangle} \newcommand{\actionvalue}[1]{q_{#1}} \newcommand{\transition}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\policy}{\pi} \newcommand{\charger}{c} \newcommand{\itervar}{k} \newcommand{\discount}{\gamma} \newcommand{\rumba}{Rumba} \newcommand{\actionnorth}{\rm N} \newcommand{\actionsouth}{\rm S} \newcommand{\actioneast}{\rm E} \newcommand{\actionwest}{\rm W} \newcommand{\chargingstations}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\basisfunc}{\phi} \newcommand{\augparam}{B} \newcommand{\valerror}{E_{v}} \newcommand{\trainerror}{E_{t}} \newcommand{\foldidx}{b} \newcommand{\testset}{\dataset^{(\rm test)} } \newcommand{\testerror}{E^{(\rm test)}} \newcommand{\nrmodels}{M} \newcommand{\benchmarkerror}{E^{(\rm ref)}} \newcommand{\lossfun}{L} \newcommand{\datacluster}[1]{\mathcal{C}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\cluster}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\bayeshypothesis}{h^{*}} \newcommand{\featuremtx}{\mX} \newcommand{\weight}{w} \newcommand{\weights}{\vw} \newcommand{\regularizer}{\mathcal{R}} \newcommand{\decreg}[1]{\mathcal{R}_{#1}} \newcommand{\naturalnumbers}{\mathbb{N}} \newcommand{\featuremapvec}{{\bf \Phi}} \newcommand{\featuremap}{\phi} \newcommand{\batchsize}{B} \newcommand{\batch}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\foldsize}{B} \newcommand{\nriter}{R} [/math]
Consider a [math]k[/math]-NN method for a binary classification problem. We use [math]k=1[/math] and a given training set whose data points characterize humans. Each human is characterized by a feature vector and label that indicates sensitive information (e.g., some sickness).
Assume that you have access to the feature vectors of the data points in the training set but not to their labels.
Can you infer the label value of a data point in the training set based on the prediction that you obtained based on your feature vector?
[math] % Generic syms \newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand{\Tt}[0]{\boldsymbol{\theta}} \newcommand{\XX}[0]{{\cal X}} \newcommand{\ZZ}[0]{{\cal Z}} \newcommand{\vx}[0]{{\bf x}} \newcommand{\vv}[0]{{\bf v}} \newcommand{\vu}[0]{{\bf u}} \newcommand{\vs}[0]{{\bf s}} \newcommand{\vm}[0]{{\bf m}} \newcommand{\vq}[0]{{\bf q}} \newcommand{\mX}[0]{{\bf X}} \newcommand{\mC}[0]{{\bf C}} \newcommand{\mA}[0]{{\bf A}} \newcommand{\mL}[0]{{\bf L}} \newcommand{\fscore}[0]{F_{1}} \newcommand{\sparsity}{s} \newcommand{\mW}[0]{{\bf W}} \newcommand{\mD}[0]{{\bf D}} \newcommand{\mZ}[0]{{\bf Z}} \newcommand{\vw}[0]{{\bf w}} \newcommand{\D}[0]{{\mathcal{D}}} \newcommand{\mP}{\mathbf{P}} \newcommand{\mQ}{\mathbf{Q}} \newcommand{\E}[0]{{\mathbb{E}}} \newcommand{\vy}[0]{{\bf y}} \newcommand{\va}[0]{{\bf a}} \newcommand{\vn}[0]{{\bf n}} \newcommand{\vb}[0]{{\bf b}} \newcommand{\vr}[0]{{\bf r}} \newcommand{\vz}[0]{{\bf z}} \newcommand{\N}[0]{{\mathcal{N}}} \newcommand{\vc}[0]{{\bf c}} \newcommand{\bm}{\boldsymbol} % Statistics and Probability Theory \newcommand{\errprob}{p_{\rm err}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{p({#1})} \newcommand{\pdf}[1]{p({#1})} \def \expect {\mathbb{E} } % Machine Learning Symbols \newcommand{\biasterm}{B} \newcommand{\varianceterm}{V} \newcommand{\neighbourhood}[1]{\mathcal{N}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrfolds}{k} \newcommand{\mseesterr}{E_{\rm est}} \newcommand{\bootstrapidx}{b} %\newcommand{\modeldim}{r} \newcommand{\modelidx}{l} \newcommand{\nrbootstraps}{B} \newcommand{\sampleweight}[1]{q^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\nrcategories}{K} \newcommand{\splitratio}[0]{{\rho}} \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\Vert {#1} \Vert} \newcommand{\sqeuclnorm}[1]{\big\Vert {#1} \big\Vert^{2}_{2}} \newcommand{\bmx}[0]{\begin{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\emx}[0]{\end{bmatrix}} \newcommand{\T}[0]{\text{T}} \DeclareMathOperator*{\rank}{rank} %\newcommand\defeq{:=} \newcommand\eigvecS{\hat{\mathbf{u}}} \newcommand\eigvecCov{\mathbf{u}} \newcommand\eigvecCoventry{u} \newcommand{\featuredim}{n} \newcommand{\featurelenraw}{\featuredim'} \newcommand{\featurelen}{\featuredim} \newcommand{\samplingset}{\mathcal{M}} \newcommand{\samplesize}{m} \newcommand{\sampleidx}{i} \newcommand{\nractions}{A} \newcommand{\datapoint}{\vz} \newcommand{\actionidx}{a} \newcommand{\clusteridx}{c} \newcommand{\sizehypospace}{D} \newcommand{\nrcluster}{k} \newcommand{\nrseeds}{s} \newcommand{\featureidx}{j} \newcommand{\clustermean}{{\bm \mu}} \newcommand{\clustercov}{{\bm \Sigma}} \newcommand{\target}{y} \newcommand{\error}{E} \newcommand{\augidx}{b} \newcommand{\task}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\nrtasks}{T} \newcommand{\taskidx}{t} \newcommand\truelabel{y} \newcommand{\polydegree}{r} \newcommand\labelvec{\vy} \newcommand\featurevec{\vx} \newcommand\feature{x} \newcommand\predictedlabel{\hat{y}} \newcommand\dataset{\mathcal{D}} \newcommand\trainset{\dataset^{(\rm train)}} \newcommand\valset{\dataset^{(\rm val)}} \newcommand\realcoorspace[1]{\mathbb{R}^{\text{#1}}} \newcommand\effdim[1]{d_{\rm eff} \left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\inspace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\sigmoid}{\sigma} \newcommand{\outspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\hypospace}{\mathcal{H}} \newcommand{\emperror}{\widehat{L}} \newcommand\risk[1]{\expect \big \{ \loss{(\featurevec,\truelabel)}{#1} \big\}} \newcommand{\featurespace}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\labelspace}{\mathcal{Y}} \newcommand{\rawfeaturevec}{\mathbf{z}} \newcommand{\rawfeature}{z} \newcommand{\condent}{H} \newcommand{\explanation}{e} \newcommand{\explainset}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\user}{u} \newcommand{\actfun}{\sigma} \newcommand{\noisygrad}{g} \newcommand{\reconstrmap}{r} \newcommand{\predictor}{h} \newcommand{\eigval}[1]{\lambda_{#1}} \newcommand{\regparam}{\lambda} \newcommand{\lrate}{\alpha} \newcommand{\edges}{\mathcal{E}} \newcommand{\generror}{E} \DeclareMathOperator{\supp}{supp} %\newcommand{\loss}[3]{L({#1},{#2},{#3})} \newcommand{\loss}[2]{L\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\clusterspread}[2]{L^{2}_{\clusteridx}\big({#1},{#2}\big)} \newcommand{\determinant}[1]{{\rm det}({#1})} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\itercntr}{r} \newcommand{\state}{s} \newcommand{\statespace}{\mathcal{S}} \newcommand{\timeidx}{t} \newcommand{\optpolicy}{\pi_{*}} \newcommand{\appoptpolicy}{\hat{\pi}} \newcommand{\dummyidx}{j} \newcommand{\gridsizex}{K} \newcommand{\gridsizey}{L} \newcommand{\localdataset}{\mathcal{X}} \newcommand{\reward}{r} \newcommand{\cumreward}{G} \newcommand{\return}{\cumreward} \newcommand{\action}{a} \newcommand\actionset{\mathcal{A}} \newcommand{\obstacles}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\valuefunc}[1]{v_{#1}} \newcommand{\gridcell}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\pair}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle} \newcommand{\mdp}[5]{\langle #1, #2, #3, #4, #5 \rangle} \newcommand{\actionvalue}[1]{q_{#1}} \newcommand{\transition}{\mathcal{T}} \newcommand{\policy}{\pi} \newcommand{\charger}{c} \newcommand{\itervar}{k} \newcommand{\discount}{\gamma} \newcommand{\rumba}{Rumba} \newcommand{\actionnorth}{\rm N} \newcommand{\actionsouth}{\rm S} \newcommand{\actioneast}{\rm E} \newcommand{\actionwest}{\rm W} \newcommand{\chargingstations}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\basisfunc}{\phi} \newcommand{\augparam}{B} \newcommand{\valerror}{E_{v}} \newcommand{\trainerror}{E_{t}} \newcommand{\foldidx}{b} \newcommand{\testset}{\dataset^{(\rm test)} } \newcommand{\testerror}{E^{(\rm test)}} \newcommand{\nrmodels}{M} \newcommand{\benchmarkerror}{E^{(\rm ref)}} \newcommand{\lossfun}{L} \newcommand{\datacluster}[1]{\mathcal{C}^{(#1)}} \newcommand{\cluster}{\mathcal{C}} \newcommand{\bayeshypothesis}{h^{*}} \newcommand{\featuremtx}{\mX} \newcommand{\weight}{w} \newcommand{\weights}{\vw} \newcommand{\regularizer}{\mathcal{R}} \newcommand{\decreg}[1]{\mathcal{R}_{#1}} \newcommand{\naturalnumbers}{\mathbb{N}} \newcommand{\featuremapvec}{{\bf \Phi}} \newcommand{\featuremap}{\phi} \newcommand{\batchsize}{B} \newcommand{\batch}{\mathcal{B}} \newcommand{\foldsize}{B} \newcommand{\nriter}{R} [/math]
Consider a binary classification problem involving data points that are characterized by feature vectors [math]\featurevec \in \mathbb{R}^{\featuredim}[/math] and binary labels [math]\truelabel \in \{-1,1\}[/math]. We have access to a labeled training set [math]\dataset[/math] of size [math]\samplesize[/math].
Show that the [math]k[/math]-NN hypothesis is obtained from the Bayes estimator by approximating or estimating the conditional probability distribution [math]\prob{\featurevec|\truelabel}[/math] via the density estimator [1](Sec. 2.5.2.)
Here, [math]{\rm vol}(R)[/math] denotes the volume of a ball with radius [math]R[/math] and [math]R_{k}[/math] is the distance between [math]\featurevec[/math] and the [math]k[/math]th nearest feature vector of a data point in [math]\dataset[/math].